E²GO : Free Your Hands for Smartphone Interaction
2 Department of Computer Science and Information Technology, La Trobe University, Melbourne, Australia
Visualization Results
Demonstration of E²GO interaction actions
The first and second rows show the actions and user tests corresponding to the E²GO. (a) Gazing at the “Bottom” area to swipe the page up. (b) Gazing at the “Top” area to swipe the page down. (c) Staring at the “Left” area to switch to the left page. (d) Staring at the “Right” area to switch to the right page. Swiftly shifting gaze from “Bottom” to “Up” to switch to the next short video. (f) Swiftly shifting gaze from “Up” to “Bottom” to switch to the previous short video. (g) Closing the right eye while keeping the left eye open to enter. (h) Closing the left eye while keeping the right eye open to return. The eye blink images of (g) and (h) mean that executing these two actions needs eye blinks. (i)-(p) correspond to the test results of the (a)-(h) action, respectively.
Demonstration of Event Data.
With event camera technology, dynamic changes in the user's eye can be captured.
Demonstration of User testing.
The first video shows the demonstrations of all interaction actions, and the second video shows the testing process.
Abstract
Current eye-gaze interaction technologies for smart phones are considered inflexible, inaccurate, and power hungry. These methods typically rely on hand involve ment and accomplish partial interactions. In this paper, we propose a novel eye-gaze smartphone interaction method named Event-driven Eye-Gaze Operation (E²GO), which can realize comprehensive interaction using only eyes and gazes to cover various interaction types. Before the interac tion, an anti-jitter gaze estimation method was exploited to stabilize human eye fixation and predict accurate and sta ble human gaze positions on smartphone screens to further explore refined time-dependent eye-gaze interactions. We also integrated an event-triggering mechanism in E²GO to significantly decrease its power consumption to deploy on smartphones. We have implemented the prototype of E²GO on different brands of smartphones and conducted a comprehensive user study to validate its efficacy, demon strating E²GO’s superior smartphone control capabilities across various scenarios.
Method
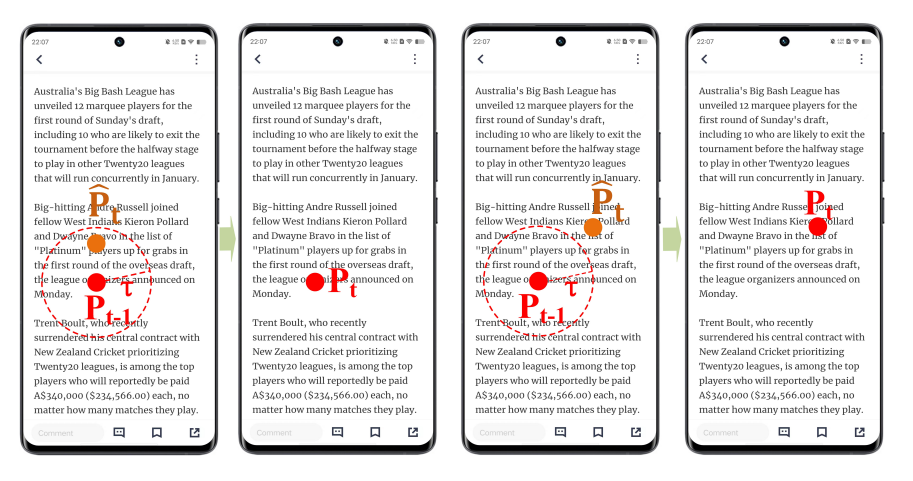
Detailed Illustration of Anti-Jitter Strategy(AJS). Left: The gaze position is a jitter and ignored. Right: the gaze position is real and kept.
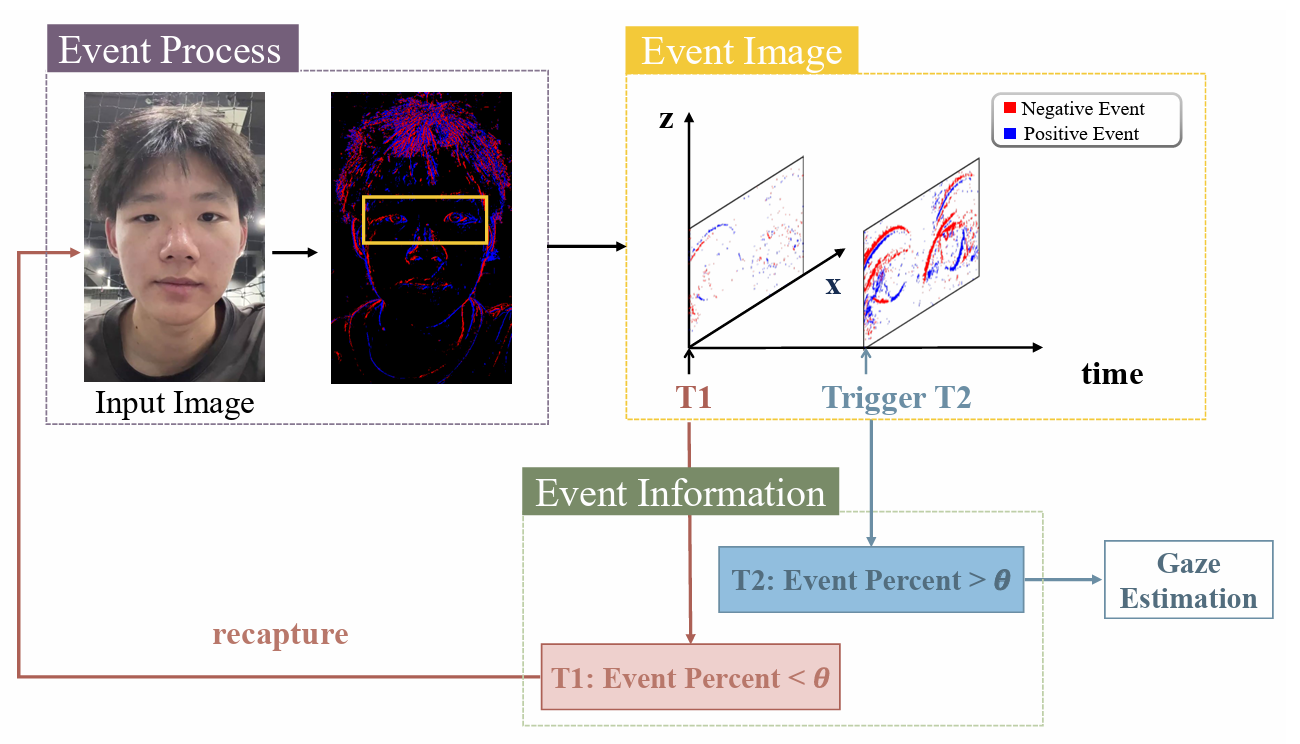
Detailed Illustration of Motion Event Detector (MED). T1: When Event Percent is less than θ, the input image is recaptured; T2: When Event Percent exceeds the threshold θ, Gaze Estimation is invoked.
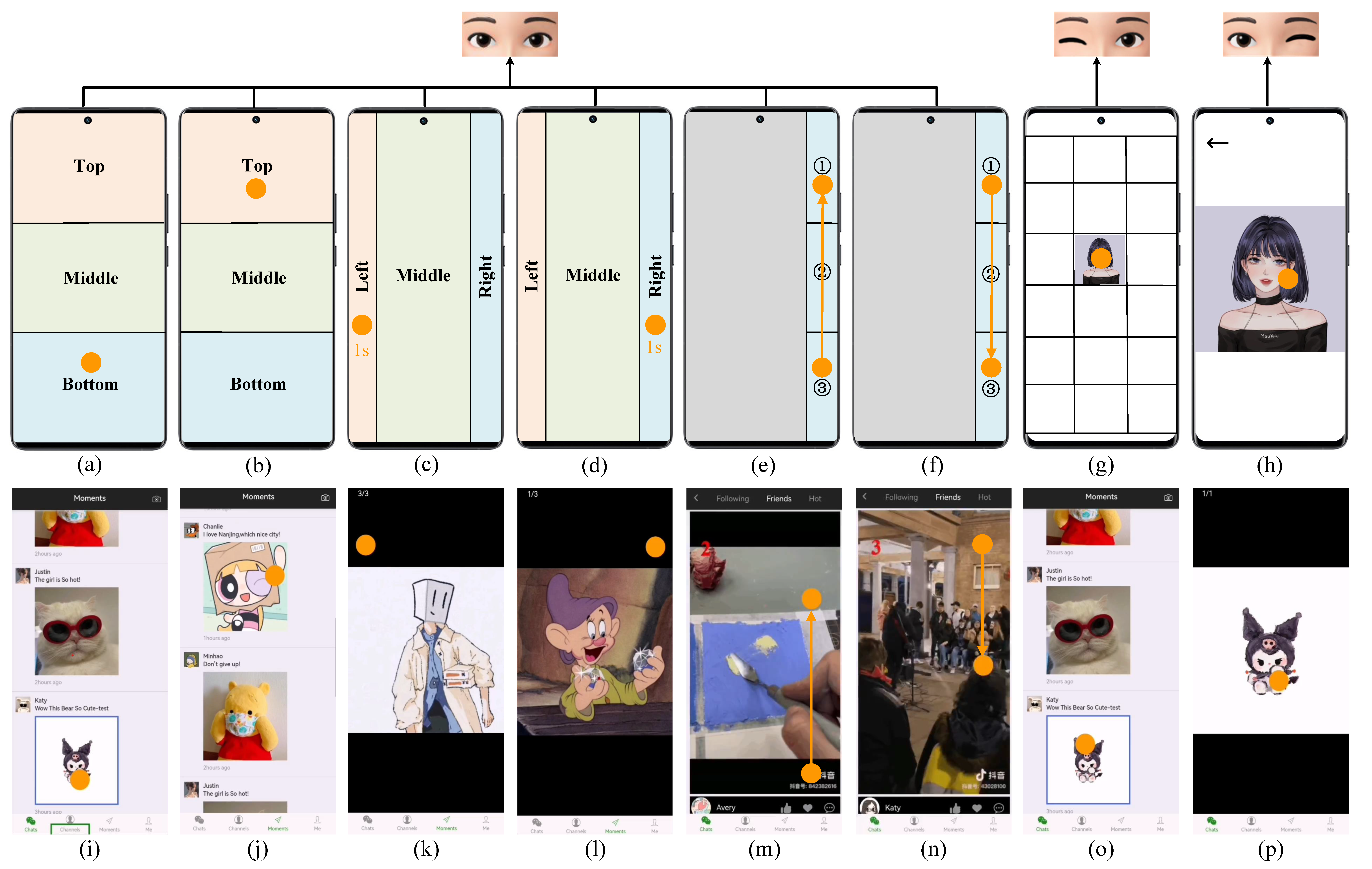
The first and second rows show the actions and user tests corresponding to the E²GO. (a) Gazing at the “Bottom” area to swipe the page up. (b) Gazing at the “Top” area to swipe the page down. (c) Staring at the “Left” area to switch to the left page. (d) Staring at the “Right” area to switch to the right page. Swiftly shifting gaze from “Bottom” to “Up” to switch to the next short video. (f) Swiftly shifting gaze from “Up” to “Bottom” to switch to the previous short video. (g) Closing the right eye while keeping the left eye open to enter. (h) Closing the left eye while keeping the right eye open to return. The eye blink images of (g) and (h) mean that executing these two actions needs eye blinks. (i)-(p) correspond to the test results of the (a)-(h) action, respectively.
Contributions
We propose an eye-gaze smartphone interaction method E²GOthatsupportsusers to perform complex interaction tasks with the help of four pairs of interactive actions.
Weintroduced an Anti-Jitter Strategy (AJS) for E²GO to ensure accurate and stable gaze positions on a screen.
We introduced a Motion Event Detector (MED) for E²GOtodecrease energy consumption significantly.
The user study results demonstrated that our proposed E²GO can realize accurate eye-gaze smartphone control in various situations.
Results
Success Rate
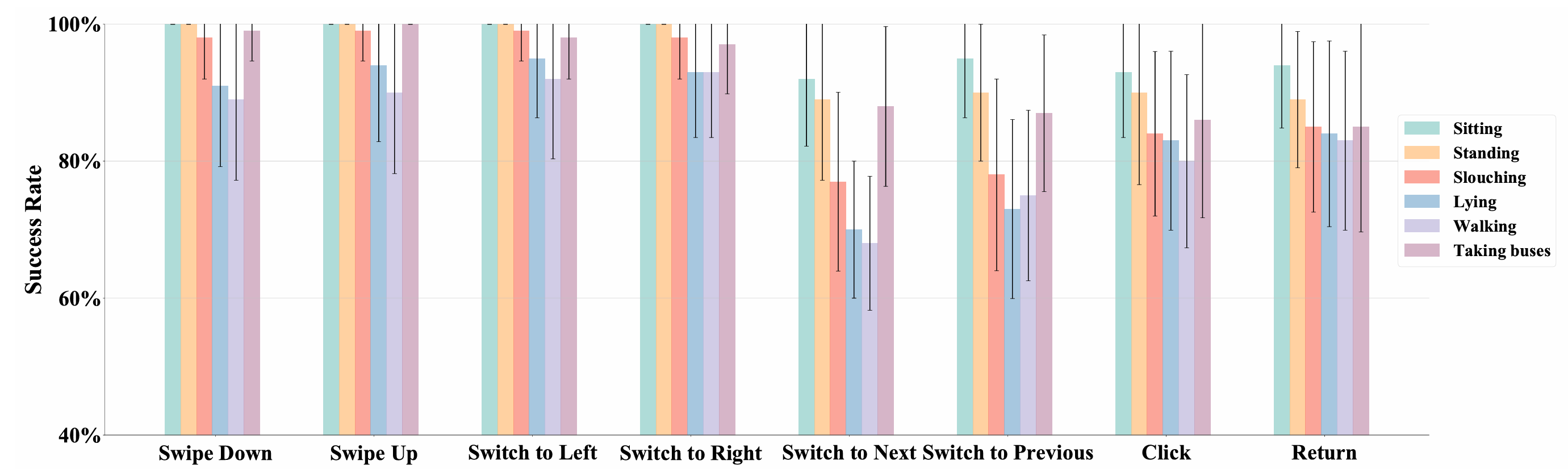
The success rates of E²GO across different postures. The bar chart represents the average success rate of users, with black error bars indicating the standard deviation.
Task Time
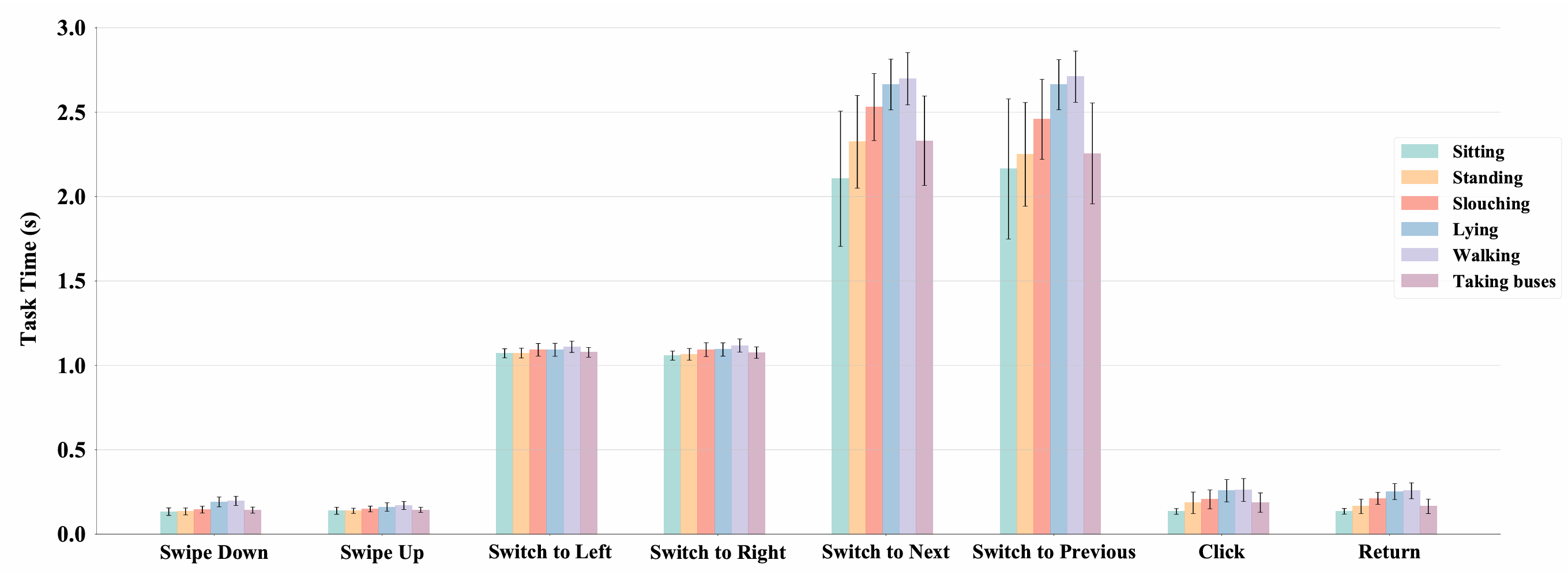
The task times of E²GO across different postures. The bar chart represents the average success rate of users, with black error bars indicating the standard deviation.
MED Studies
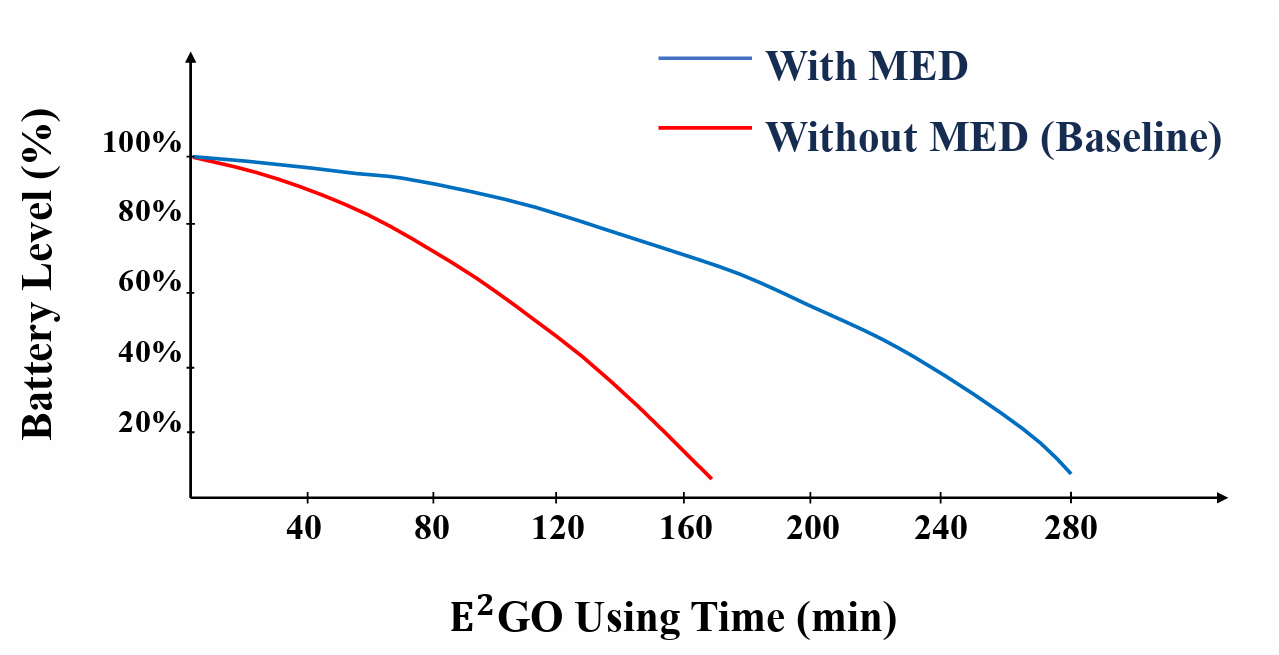
A comparison of the usage time for the battery life with and without MED for E²GO.